What is stud welding?
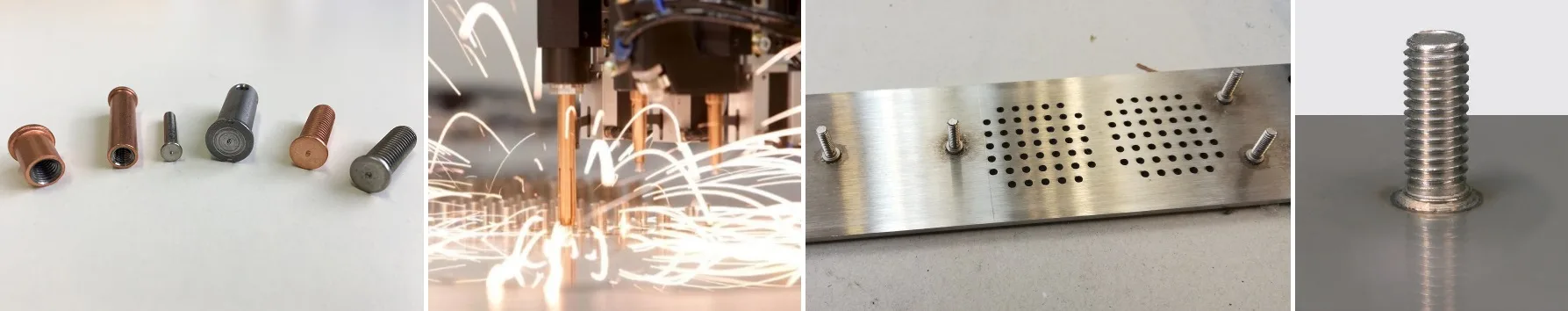
Stud welding is an instantaneous single-side fixing technique that allows studs, tapped studs, pins and other metal fasteners to be welded on sheet metal or other flat metal objects, by means of an electric arc, ignited between the end of the stud and the surface of the workpiece, and the subsequent application of a pressing force.
Advantages
- Quick and easy operation leads to increased productivity
- Improved weld quality and uniformity, thanks to complete fusion of stud’s cross-section
- High strength of the welded joint (if the welding process is well-executed, the joint can withstand a greater static load than the stud or workpiece)
- No marking or blackening on workpiece backside, hence re-working is not necessary (high aesthetic quality)
- Guaranteed weldability even on thin sheet metal
- No alteration of mechanical properties caused by drilled holes
- No filler materials necessary (in particular, for capacitive discharge welding, not even inert gases are required)
- No welding templates required with automatic machines
- High repeatability and elimination of perpendicularity errors with automatic machines
- Cost reduction (less manpower, shorter production time, minimum waste)

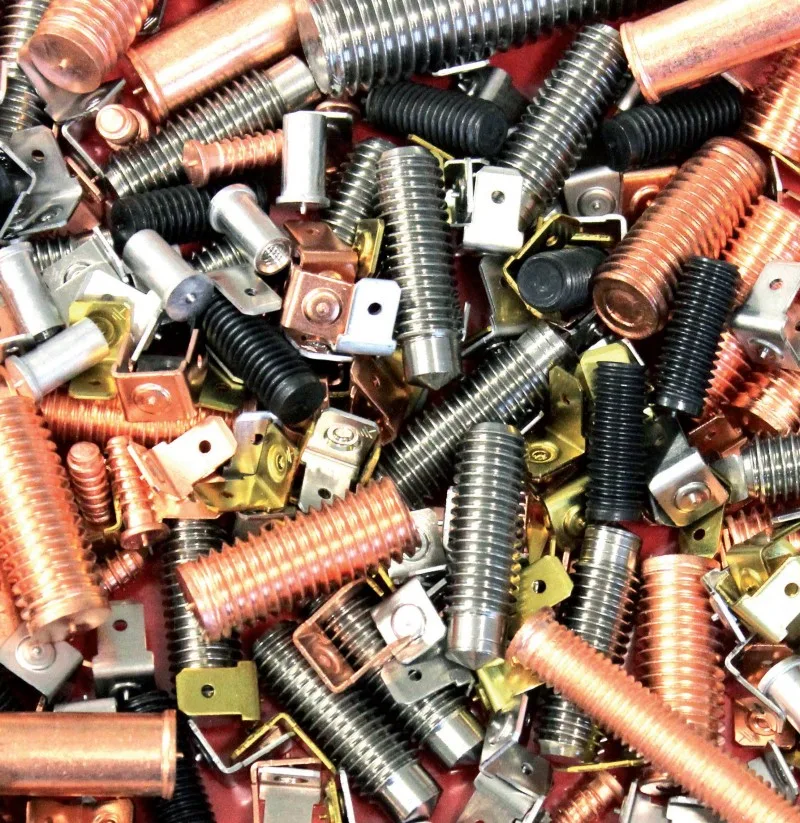
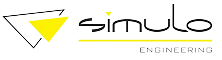
Welding elements
- Threaded studs
- Studs with internal thread
- Unthreaded studs (pins)
- Coarse threaded studs
- Insulation nails and pins
- Earth tags
- Balls
- Stainless steel nuts (with SRM Technology®)
SRM Technology® is a registered trade mark of Heinz Soyer Bolzenschweißtechnik GmbH.
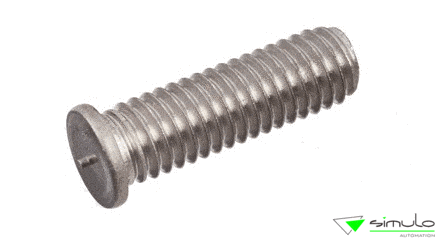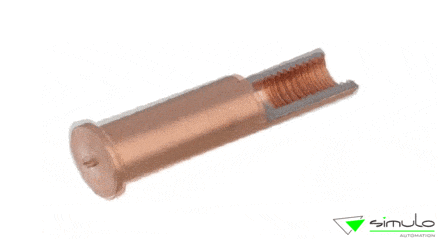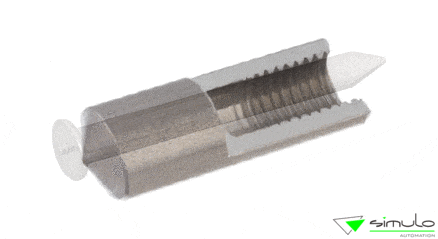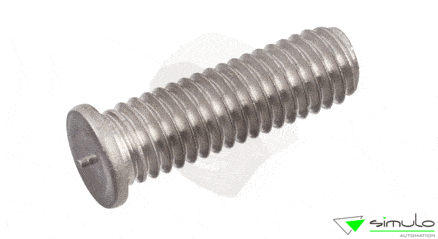
Applications

Elevator panels

Plates and panels

Steam irons

Commercial cooking equipment

Household appliances components

Cooker hoods

Coffee machines

Vending machines

ATM machines

Shower heads

Lighting fixtures

Automotive components

Electrical enclosures and cabinets

Shipbuilding

HVAC insulation/soundproofing

Constructions